Internal and external rotation of the knee is a popular test especially in ski-ing populations. The popliteus and hamstrings muscles play a significant role in rotating the knee (internally and externally) to aid unlocking and locking the knee.
It should be noted that this position stretches the ligaments at t the rear of the knee and can impinge the meniscus (cartilages) at the posterior horns.
This could be the effect you want some patient populations (like ski-ing) but in many cases can lead to injury.
Care should be exercised if using this test.
Supine Lying position:
In this position there is the increased innate thoracic and pelvic stability (little rotation occurs) but the angle of the knee has to be considered with the knee at 90 degrees results tend to be higher than the other most popular angle 45 degrees.
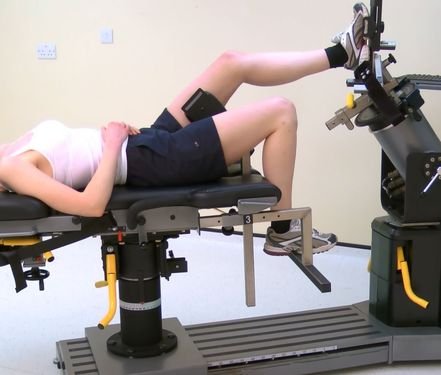
Stabilisation:
Lying: in the lying position stabilisation usually involves holding the bed handles. Most manufacturers supply a thigh / calf stabiliser. Use the pelvic strap.
Attachments:
The footplate supplied with the machine should fully stabilise the foot it is likely the foot will pull to dorsi flexion during the test so care should be used to full tighten any straps
Axis of rotation:
The axis of rotation goes from the machine and extends through the center of the calcaneous (see below). To check the alignment simply rotate the foot and ensure the knee does not lift from the stabiliser.

Anatomical zero:
Foot points to roof.
Range of motion:
Large individual variations exist in the amount of movement. The ROM should be between 30-50 degrees internal rotation and 20-40 degrees external rotation.
Gravity correction:
The effects of gravity are negligible in this position in fact some manufacturers use a counter balance rather than instrumented correction.
Speeds:
Speeds tend to be lower in internal external rotation of the knee with multiples of 30 being common. However, any speed from 30-240 degrees/second could be considered representative of the speed of subtalar movement during walking/running. A mid range speed for ordinary subjects is 45 degrees per second which will offer good results.
Generally it is accepted that speeds of 30 degrees/second and multiples of this should be used.
Knee Internal / External Rotation Protocols:
Muscles involved:
Hamstrings and Gastrocnemius
| Strength Test Protocols | General | Patients | Athletes | Research |
| Contraction Cycle | con/con | con/con | con/concon/ecc | con/conecc/ecc |
| Speed/s | 30 – 60 | 30 | 30-180 | 30-180 |
| Trial Repetitions | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Repetitions | 10 | 10 | 10 | 5 |
| Sets | 3 | 3 | 4 | up to 9 |
| Rest between sets | 20-30 secs | 20-30 secs | 20-30 secs | 20 secs |
| Rest between speeds | 2 minutes | 2 minutes | 2 minutes | 2-5 minutes |
| Rest between sides | 5 minutes | 5 minutes | 5 minutes | 5 minutes |
| Feedback | nil | nil | nil | nil |
| Endurance Test Protocols | General | Patients | Athletes | Research |
| Contraction Cycle | con/con | con/con | con/concon/ecc | con/conecc/ecc |
| Speed/s | 60 | 30 | 60-180 | 60-180 |
| Trial Repetitions | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Repetitions | Max | Max | Max | Max |
| Sets | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Rest between sets | N\A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Rest between speeds | 10-15 mins | 10-15 mins | 10-15 mins | 10-30 mins |
| Rest between sides | 5 mins | 5 mins | 5 mins | 5 mins |
| Feedback | nil | nil | nil | nil |
| Strength Exercise Protocol | General | Patients | Athletes |
| Contraction Cycle | con/con | con/con | con/ecc |
| Speed/s | 30 up to 60 | 30 | 30-180 |
| Trial Repetitions | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Repetitions | 10 | 10 | 14 |
| Sets | 6 | 6 | up to 12 |
| Rest between sets | 30-60 secs | 30-60 secs | 30 secs |
| Rest between speeds | 2 mins | 2 mins | 2 mins |
| Rest between sides | Nil | Nil | Nil |
| Feedback | bar | bar | bar |
| Endurance Exercise Protocol | General | Patients | Athletes |
| Contraction Cycle | con/con | con/con | con/con |
| Speed/s | 60 | 30 | 60-180 |
| Trial Repetitions | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Repetitions | Max | Max | Max |
| Sets | 1-3 | 1 | 1-3 |
| Rest between sets | 5-10 mins | N/A | 5-10 mins |
| Rest between speeds | 10-30 mins | N/A | 10-30 mins |
| Rest between sides | Nil | Nil | Nil |
| Feedback | bar/pie chart | bar/pie chart | bar/pie chart |
Notes:
Test the uninvolved or dominant limb first. Extreme care must be taken to not damage the knee in this pattern.
Interpretation:
In the knee it is normal to look at the ratio between the right and left sides there should be a 0-10% difference between the sides. Anything beyond this would indicate a muscle imbalance which would be best corrected.
Eccentric results are generally 30% higher than concentric within the same muscle.
Concentric/concentric: internal/external rotation ratio should show a external rotation dominance of 10 percent.
Peak torque occurs in the internal rotators at 20 degrees and in the external rotators at 2 degrees (Hester & Falkel 1984).
Normative values:
| All values Pt ftlbs | DominantInternal | Non DominantInternal | DominantExternal | Non DominantExternal | |||
| Ostering et al. (1980) | knee angle | M | 18-35 | ||||
| 30 deg sec | 90 | 89.7 | 102.7 | 101.3 | 111.4 | ||
| 30 deg sec | 45 | 78.1 | 77.4 | 83.2 | 81.0 | ||
| Hester & Falkel (1984) | 90 | M | 18-35 | ||||
| 30 | 28 | 24.7 | 28.2 | 25.6 | |||
| 60 | 25.4 | 22.8 | 25.6 | 24.1 | |||
| 120 | 20 | 18.5 | 20.1 | 19.2 | |||
| 180 | 16.2 | 15.1 | 16.9 | 15.5 |
| PTBW ftlbs | LeftInternal | LeftExternal | RightInternal | RightExternal |
| 30 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 16 |
| 60 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 15 |
| 120 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 |
| 180 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 10 |